Learning Outcomes
i. Upon successful completion of this lesson, students will be able to:
ii. Identify and explain the purpose of menus, toolbars, and dialog boxes in computer applications.
iii. Navigate through menus to access various application features.
iv. Utilize toolbars for quick access to frequently used functions.
v. Effectively interact with dialog boxes to provide input and customize settings.
Introduction
In the realm of computer applications, menus, toolbars, and dialog boxes serve as essential tools that facilitate user interaction and enable seamless navigation. These components play a pivotal role in enhancing the user experience by providing a structured and intuitive interface for accessing application features and performing tasks.
i. Menus
Menus are hierarchical structures that organize application features into categories and subcategories. They typically appear at the top of the application window and can be accessed by clicking the menu name or using keyboard shortcuts. Menus provide a comprehensive overview of available features, allowing users to locate the desired function quickly and efficiently.
ii. Toolbars
Toolbars offer a compact and easily accessible collection of icons or buttons that represent frequently used functions within an application. They are often located below the menu bar or can be docked to the sides of the application window. Toolbars provide a convenient way to execute common tasks without having to navigate through menus, thereby streamlining the workflow and enhancing productivity.
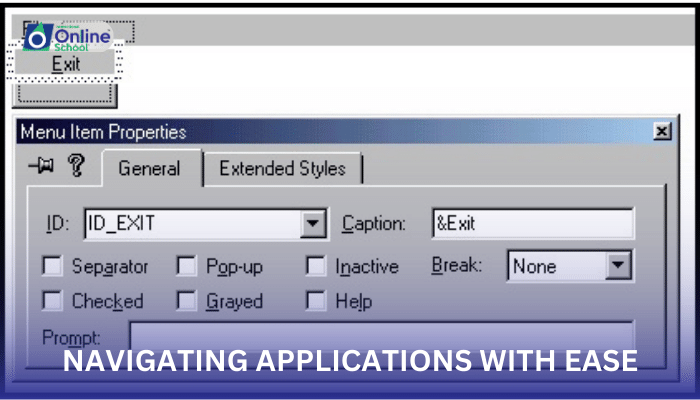
iii. Dialog Boxes
Dialog boxes are temporary windows that appear to prompt users for input, provide additional information, or allow customization of settings. They typically contain a combination of text fields, buttons, and checkboxes that enable users to interact with the application and provide the necessary information or make desired changes. Dialog boxes play a crucial role in ensuring user input accuracy and facilitating control over application behavior.
Examples
Menus: When using a word processing application, the "File" menu might contain options for creating, opening, saving, and printing documents.
Toolbars: In a web browser, the toolbar might include buttons for navigating to previous or next pages, refreshing the current page, and performing searches.
Dialog Boxes: When opening an image editing software, a dialog box might appear allowing users to select the file format for saving the edited image.
Menus, toolbars, and dialog boxes are fundamental components of computer applications that simplify user interaction and enhance productivity. By understanding their purpose and functionalities, users can navigate applications effectively, access features with ease, and customize settings to suit their preferences. As technology continues to evolve, the role of these interface elements will remain essential in ensuring user-friendly and productive computing experiences.